Non-random patterns and enrichment patterns
COVID-19 vaccines immediate onset Autoimmune Disease adverse events in VAERS
Non-random patterns and enrichment patterns

“Darrell O. Ricke, M.S., Ph.D.
Oct 16, 2023
My article on immediate onset autoimmune disease adverse events with immediate onset following vaccination is published online here: Ricke, GTM (2023) https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1455
This post focuses on 30+ autoimmune disease adverse events enriched following COVID-19 vaccinations. The VAERS data has the following limitations: (1) only a subset of actual adverse events are captured (estimated at 1 in 241 in the above article) and (2) reported adverse events include background frequency adverse events. If the adverse events are all background and the number of dose 2 shots is slightly less than the number of dose 1 shots for COVID-19 mRNAs, then the ratio of [dose 2/dose 1] should be less than 1.0 for autoimmune disease adverse events other than random fluxuations. So observing excess autoimmune disease adverse events following dose 2 shots greater than dose 1 shots is not likely to occur by chance very often.
Figure 3 (from article). COVID-19 vaccines dose 2 versus dose 1 autoimmune diseases adverse events ratios – autoimmune diseases label: postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS).
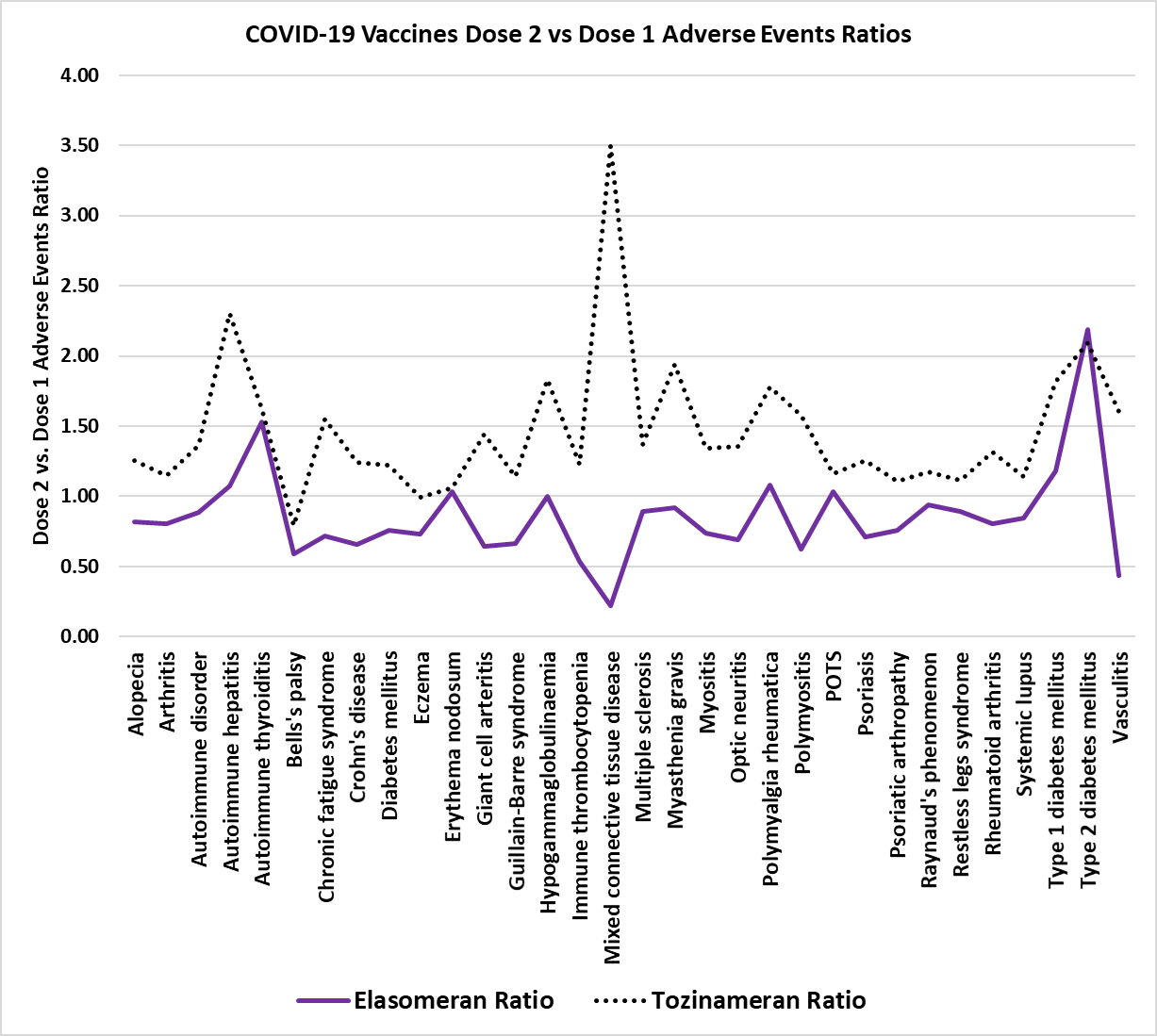
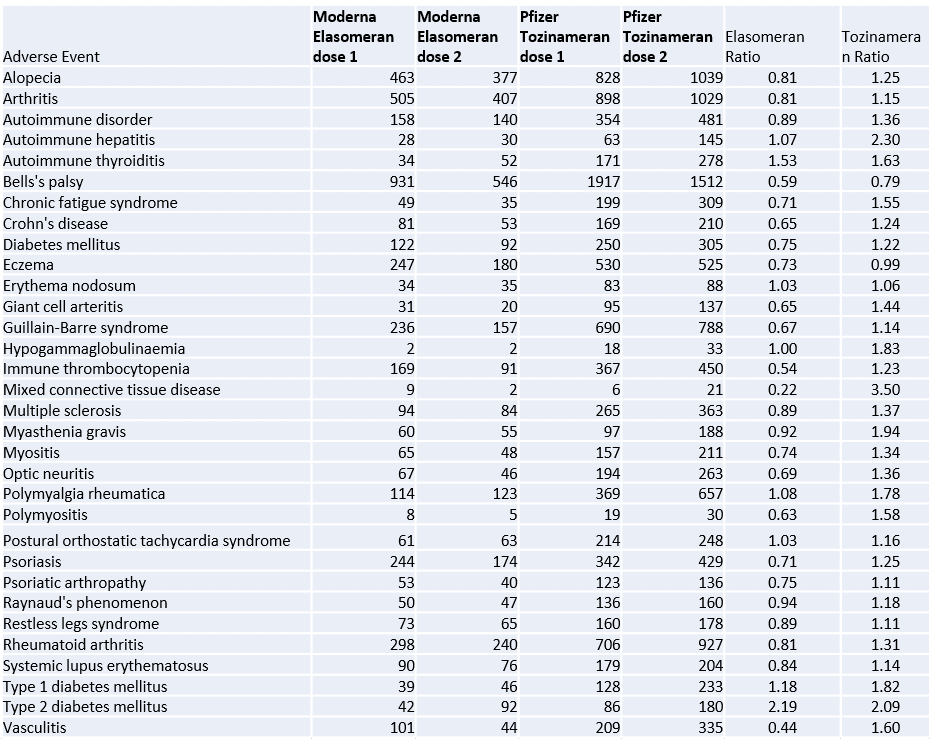
The Moderna Elasomeran mRNA vaccine has 100 micrograms of mRNA with 4 weeks between doses while the Pfizer Tozinameran vaccine has 30 micrograms of mRNA with 3 weeks between doses. A total of 30 of 32 autoimmune adverse events for dose 2 for Pfizer Tozinameran have ratios greater than 1.0 with 29 greater than 1.1. In comparison, the Moderna Elasomeran vaccine shows 7 with ratios greater than 1.0 and 3 greater than 1.1. This is evidence of a non-random enrichment frequency for the majority of these autoimmune disease adverse events and the null-hypothesis of these being background associations should be rejected for Tozinameran.
Figure 4 (above article). The age of COVID-19 vaccinees experiencing various autoimmune disease adverse events.
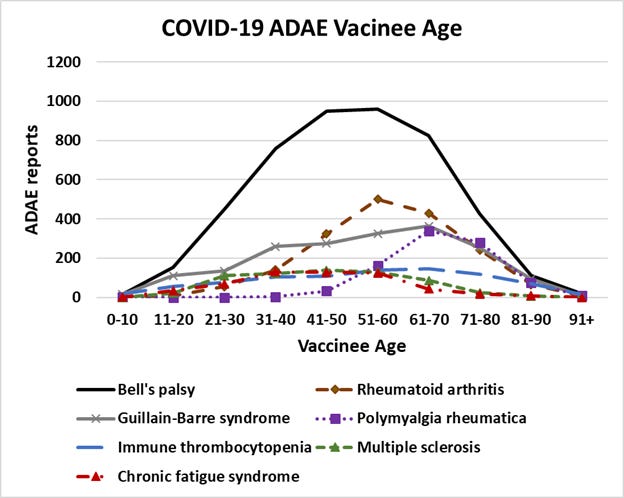
From Figure 4, it is possible to infer that there is not a specific age associated pattern. Polymyalgia rheumatica is known to affect older adults. The association of autoimmune disease adverse events with COVID-19 vaccines appear to be generally, a non-specific association. The pattern could be these adverse events are being triggered in individuals with existing risk conditions.
For the individual COVID-19 vaccines, does the distribution of autoimmune diseases reflect the ratios of the vaccines administered? Additional non-random patterns are observed in Table 1.
Table 1 (from article). Autoimmune adverse events by doses of COVID-19 vaccines.
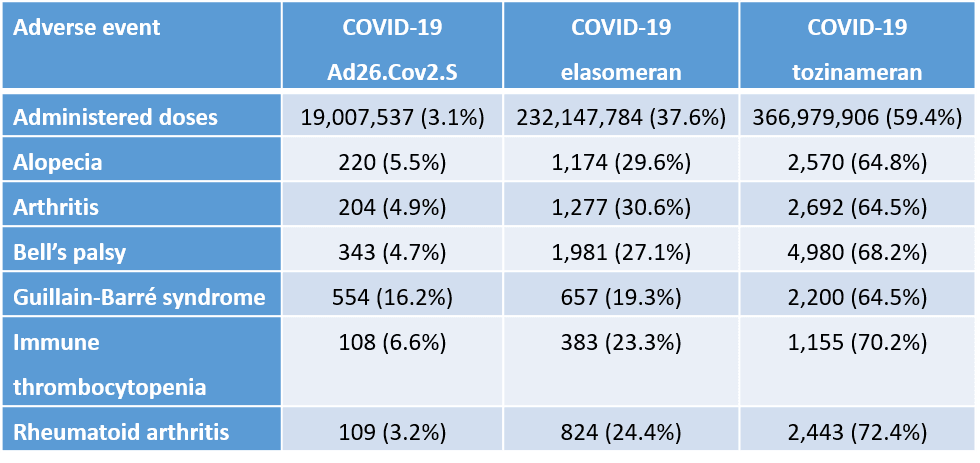
In Table 1, Guillain-Barré syndrome represents 16.2% of the adverse events for Ad26.Co2.S but the vaccine only represents 3.1% – a 5.2-fold higher than expected by distribution of doses between vaccines. Excess immune thrombocytopenia is a known rare adverse event for adenoviral COVID-19 vaccines that can be life threatening.
In the article, I calculate the under-reporting factor (URF) for COVID-19 vaccines to possibly be as high as 1 in 241 based on the number of common adverse events reported (headache, fever, etc.). The following enrichment fequencies are all higher than background without applying a URF correction factor. For purposes of illustration, a common used URF of 45 is illustrated in the following table. Note that these estimates are for reported onsets within 24 hours of vaccination!

In summary, COVID-19 vaccines have non-random enrichment patterns of association for many autoimmune diseases. Surprisingly, many of these autoimmune disease adverse events are occurring within 24 hours of vaccination (day 0). In general, these pattern appears to be non-specific (e.g., not likely just cross-reacting epitope antigens, etc.). My initial hypothesis is that many of these patterns may result from the very high reactogenicity level of these COVID-19 mRNA and adenoviral vaccines creating very strong immune responses pushing some at risk individuals over disease onset thresholds for these autoimmune diseases. If correct, then all mRNA and adenoviral vaccines and therapeutics may also exhibit similar patterns of enrichments for autoimmune disease adverse events.
Note: Geoff Pain, PhD points out endotoxins and possible process 2 for at least one of these vaccines to consider, see Process 2 post.
Added note:
Back in March 6, 2023, Ronald Kostoff published an op-ed on TrialSiteNews ARE COVID-19 VACCINE-INDUCED ADVERSE AUTOIMMUNE EVENTS RARE?“
Leave a Reply